Samsung’s $6.4 Billion New Gen Chip Grant: Biden’s AI Drive Against Asian Competition

The US awards Samsung a massive grant to build advanced chip plants in Texas, aiming to strengthen chip output and reduce reliance on Asia. l Source: Rebecca Noble/Getty Images
Key Takeaways
- The Biden administration grants Samsung $6.4 billion to build chip plants in Texas.
- This move – along with other investments under the Chips and Science Act – aims to reduce reliance on Asian competitors.
- The US investment might lead to oversupply and price drops, prompting similar subsidy programs from other countries.
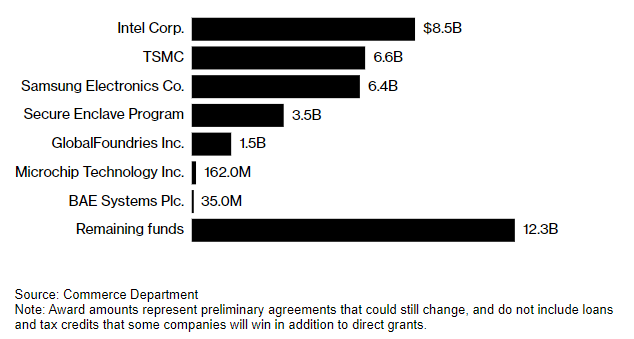
The Biden administration intends to grant Samsung Electronics up to $6.4 billion to expand chip production in Texas, as a strategic measure to enhance domestic semiconductor manufacturing within the United States.
This decision represents the most recent step in Biden’s broader initiative, outlined in the Chips and Science Act, aimed at reducing reliance on Asian competitors in the artificial intelligence (AI) chip race. Notably, this effort is occurring even as the administration continues to depend on Asian companies to construct factories and manufacture chips within the United States.
Samsung Gets $6.4 Billion
The South Korean conglomerate plans to invest over $40 billion in several initiatives. These include building two foundry fabrication sites capable of producing advanced 4-nanometer and 2-nanometer logic chips. This ambitious project also includes establishing a research and development facility and an advanced chip packaging plant in Taylor, Texas. It will focus on high bandwidth memory chips essential for AI applications.
Additionally, the grant will facilitate the expansion of Samsung’s existing chip manufacturing facility in Austin, Texas. This facility will support key sectors such as aerospace, defense, and automotive industries, the Commerce Department said .
Unlike Intel and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing, both of which are slated to receive substantial grants under the Chips Act, Samsung has chosen not to utilize loans or loan guarantees. Instead, the project is anticipated to benefit from an investment tax credit, projected to cover up to 25% of qualified capital expenditures, according to US officials.
The Taylor initiative further enriches the flourishing semiconductor ecosystem in Texas, complementing significant investments from Texas Instruments within the state and Samsung’s existing manufacturing facility in Austin.
One of the fabrication plants in Taylor would commence production in 2026, with the other slated for operation in 2027, a senior administration official revealed . Notably, Samsung initially announced that the Taylor plant would commence production in the latter half of 2024.
Biden’s Push To Beat Asian Competition
Samsung’s recent accolade represents a significant milestone in President Biden’s ongoing efforts to fortify the US semiconductor industry, aligning closely with the 2022 Chips and Science Act. This achievement stands out as one of the largest awards granted under the program, which earmarked $39 billion in grants. It also extended further support through loans and guarantees totaling $75 billion.
These incentives are strategically designed to encourage semiconductor companies to establish manufacturing facilities within the United States, aiming to reverse a longstanding trend of offshore production that has persisted for decades.
Intel has already secured a preliminary agreement for nearly $20 billion in grants and loans. Which came before Samsung Electronics’ funding of $6.4 billion. Additionally, the Commerce Department has conferred three awards to companies specializing in older-generation chips, with plans underway to unveil a multibillion-dollar package for Micron Technology in the coming weeks.
Since President Biden’s inauguration, corporations have pledged upwards of $200 billion in investments within the US, with significant hubs emerging in Arizona, Texas, and New York.
The Chips And Science Act State Of Art
The Chips and Science Act is a crucial step forward for American semiconductor research and development. It aims to reinforce US leadership in a technology vital for industries like automotive, household appliances, and defense. Despite pioneering the semiconductor, the US currently produces just 10% of the world’s chips, largely relying on East Asia for 75% of its supply. This legislation aims to attract significant private sector investment, crucial for national defense and other key sectors.
Furthermore, the Act aims to uphold and enhance the United States’ scientific and technological prowess. Over the past decades, economic growth has disproportionately favored coastal regions, leaving many communities marginalized. The Act seeks to foster innovation across all corners of America. It aims to ensure opportunities in science and technology reach historically underserved populations.
Concerns have arisen about the Act’s impact on tech industries in other regions, particularly in East and Southeast Asia. The latter are major players in semiconductor exports. While US subsidies aim to address this concentration, boosting domestic production may disrupt current export markets. In response, countries like the EU, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea have initiated their own subsidy programs. This may potentially lead to global oversupply and price declines.
Efforts to diminish Chinese involvement in supply chains also challenge Asian suppliers, given China’s significant role as a silicon supplier. Although the long-term effects are uncertain, ongoing consultations led by the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework’s Supply Chain Council aim to tackle these concerns. They also want to foster collaboration among member countries to diversify supply sources and uphold open trade.


