Crypto 101: Beginner’s Guide to Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps

Atomic swaps mean the ability to exchange digital assets across different blockchain networks without the involvement of central parties. This has piqued the interest of the crypto-community since early 2017. Atomic swaps are inherently different from decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges because they represent a novel cryptographic protocol. Here two parties seamlessly and securely exchange bitcoin or other digital assets without the risk of theft.
Atomic swaps create a cryptographically encrypted escrow account that instantaneously refunds users if the trade does not occur. Even if the trade between two traders is aborted, they receive their funds back.
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: Protocol and Gateway
Centralized platforms and decentralized applications (dApps) do not need to perform atomic swaps. However, certain protocols are needed to perform the transaction between two users on two different blockchain networks in a secure manner.
One such blockchain protocol is Waves that enables large-scale atomic swaps between different blockchains.
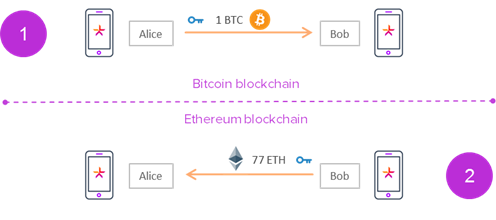
This protocol creates a system to enable the receiving and sending of tokens over different blockchains. Thus, when Alice sends 1BTC to Bob, and he sends 77ETH back to her, the same system should be able to store both types of tokens. This is a true atomic swap.
In comparison, several exchanges which provide single password access to their users and allow them to hold several types of cryptocurrencies in a single wallet follow a different mechanism. At the backend, new wallets are created as per the requirement of the user and are mapped to the user’s profile and password. This is not a true atomic swap because there is no cross-chain communication.
In an interview, Ethan Heilman, the founder of Commonwealth Crypto and research fellow at Boston University focusing on research and development on blockchain technology, stated:
“While cross-chain atomic swap protocols for bitcoin-like blockchains have been known for many years very little work has been done to make such atomic swaps practical and easy for traders to use. I’m not aware of any software which currently enables users to easily perform cross-chain atomic swaps.”
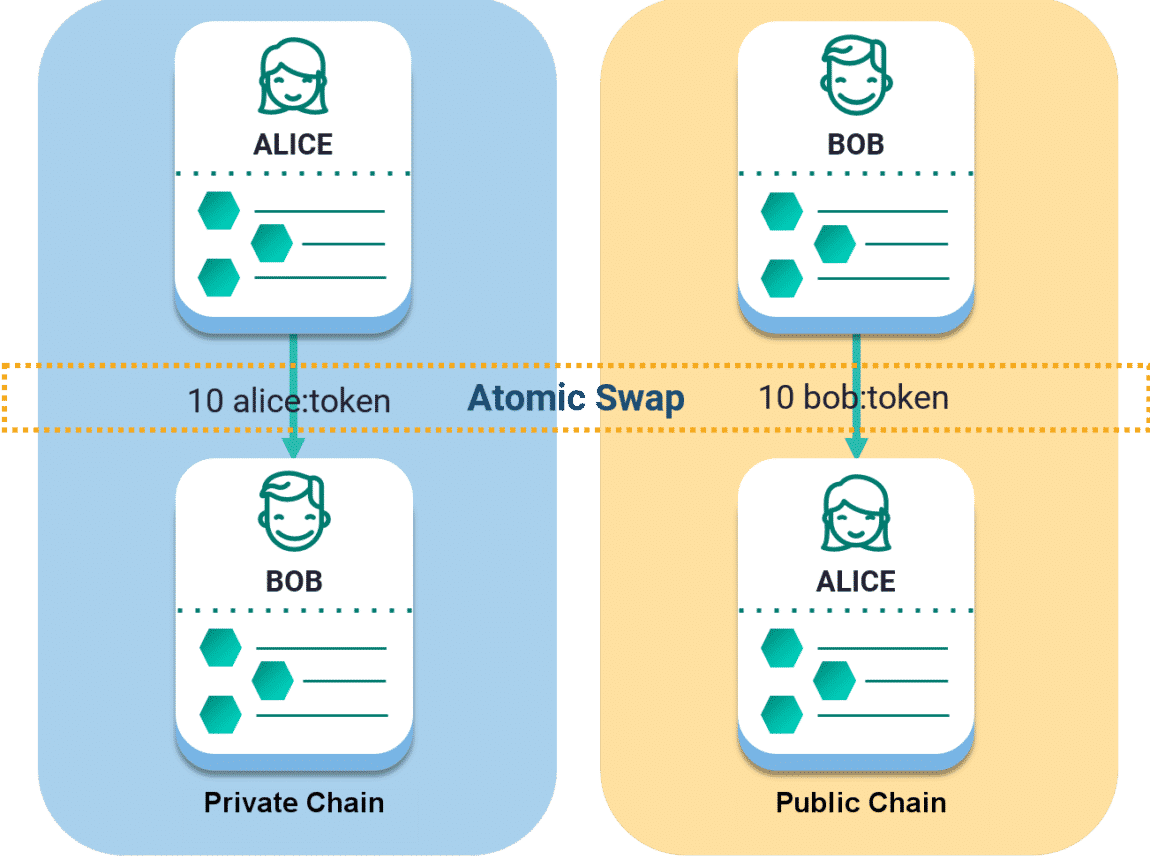
Existing Gateway Systems
Gateway systems are bridges for the exchange of tokens. The existing gateway systems allow the crossing over of one kind of token only. To transfer another type of token, another gateway system has to be built. This step is redundant and wastes gas as well. Atomic swaps will replace this multiplicity of gateway systems with a single gateway system to allow the transfer of all type of tokens.
Usually, gateways allow tokens to be easily integrated into different exchanges which support third-party nodes or are based on their own blockchains. The more commonly used term for these is payment gateways.
(Source: inves8r.com)
The development team of the Waves platform is building a network that can handle gateway systems to streamline the process of engaging in atomic swaps with other major blockchain networks like Ethereum.
Heilman stated that while the approach of Waves platform is valuable, there are security concerns which the developers of the system will have to address and improve. He further emphasized that atomic swap protocols that are able to process digital asset trades across bitcoin, litecoin, and other public blockchain networks have been well studied and are very secure.
Cross Chain Atomic Swaps in Action
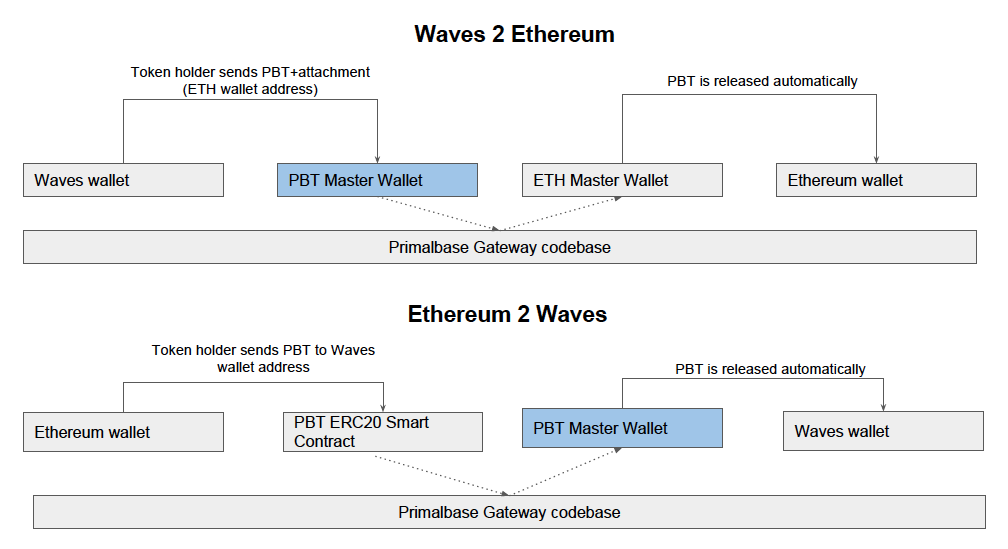
A Waves-based blockchain project, Primalbase, used cross-chain atomic swaps to simplify crypto-payments to book office spaces . They created Etherswap to enable a single gateway for the transfer of ERC20 and WAVES tokens. In this case, Etherswap is the gateway system that enables transactions without the need to create two different gateway systems for two different blockchains.
*Etherswap is a token transfer system between the Ethereum blockchain (contract ERC20) and the Waves blockchain, to enable the conversion of Primalbase tokens (PBT) from Waves tokens to ERC20 tokens, and the other way around.
To simplify, wallets are introduced on each blockchain. The Ethereum ERC20 wallet accepts the ERC20 token (ERC20 PBT in our case) while the Waves wallet accepts the Waves asset (Waves compliant PBT in our case).
The tokens on both blockchains are distinctive assets, but the token supply is controlled by the issuer.
So, PBT becomes a gateway token that can be transferred over two blockchains — Waves and Ethereum.
The token flow follows the following mechanics:
- The user creates a transaction to send tokens to either Waves or Ethereum wallet address. To send tokens to an Ethereum address, the user must have tokens in his/her Waves wallet and vice versa.
- To send Waves-compliant tokens to Ethereum, the user sends the tokens to the designated Ethereum wallet address and vice versa.
Earlier, to exchange the token of one blockchain, e.g., bitcoin for a token of another blockchain, say ether, one had to go to exchanges or services such as ShapeShift.
Now, the transactions are completely peer-to-peer with zero intermediaries in between. This is more secure than DEXs which can be compromised to divert funds sent to the hot wallets for trading.
What Does the Industry Think?
Elena Goldberg, the head of an Amsterdam R&D Lab, said in an interview:
“We helped develop token Gateway functionality from Waves to Ethereum and back. It allows token holders to store their tokens in different wallets which support Ethereum. Moreover, it opens doors to ERC20 exchanges for the token.”
Waves founder and CEO Sasha Ivanov explained:
“[atomic swaps through a gateway] is a great way to transfer your tokens from Ethereum to Waves blockchain and the other way around. So if you’re an Ethereum user and you are accustomed to using Ethereum and you don’t really want to look into new blockchains, you can use Primalbase tokens.”
Conclusion
Atomic swaps promise to completely eliminate counterparty risk and the possibility of theft. Gateway systems such as the one explained above are neither an exchange, a blockchain or a payment processor.
As Heilman said, atomic swaps are most useful in allowing users to trade without counterparty risk:
“You could use cross-chain atomic swaps for a decentralized exchange. However, I believe they are best suited for allowing users to trade on a centralized exchange while eliminating the counterparty risk of that exchange being hacked or shut down. This is because centralized exchanges support a very high volume of trades allowing fast trades, liquidity, and accurate prices. For these reasons Commonwealth Crypto is partnering with centralized exchanges.”
Etherswap, Commonwealth Crypto, Primalbase, and Waves are some of the early adopters of atomic swaps and projects that have started to improve the infrastructure around the technology to improve its usability and bolster its adoption by users in the cryptocurrency market.
Stay tuned for a follow-up article exploring atomic swaps using the Lightning Network (LN).
Featured Image from Shutterstock