Why Bitcoin Plunged to 15th in China’s Bizarre Crypto Rankings

Bitcoin keeps falling in China's government-compiled crypto rankings. | Source: Shutterstock
China Electronic Information Industry Development (CCID), which operates directly under the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China, released its crypto rankings for March, featuring top 35 crypto assets in the likes of Ethereum, Bitcoin, EOS, TRON, and Ontology.
Bitcoin dropped from 13th to 15th since last month while TRON climbed up the rankings to secure the number 2 spot. EOS topped the rankings, and Ethereum fell behind TRON at third.
EOS & TRON Trump Bitcoin in China Blockchain Rankings
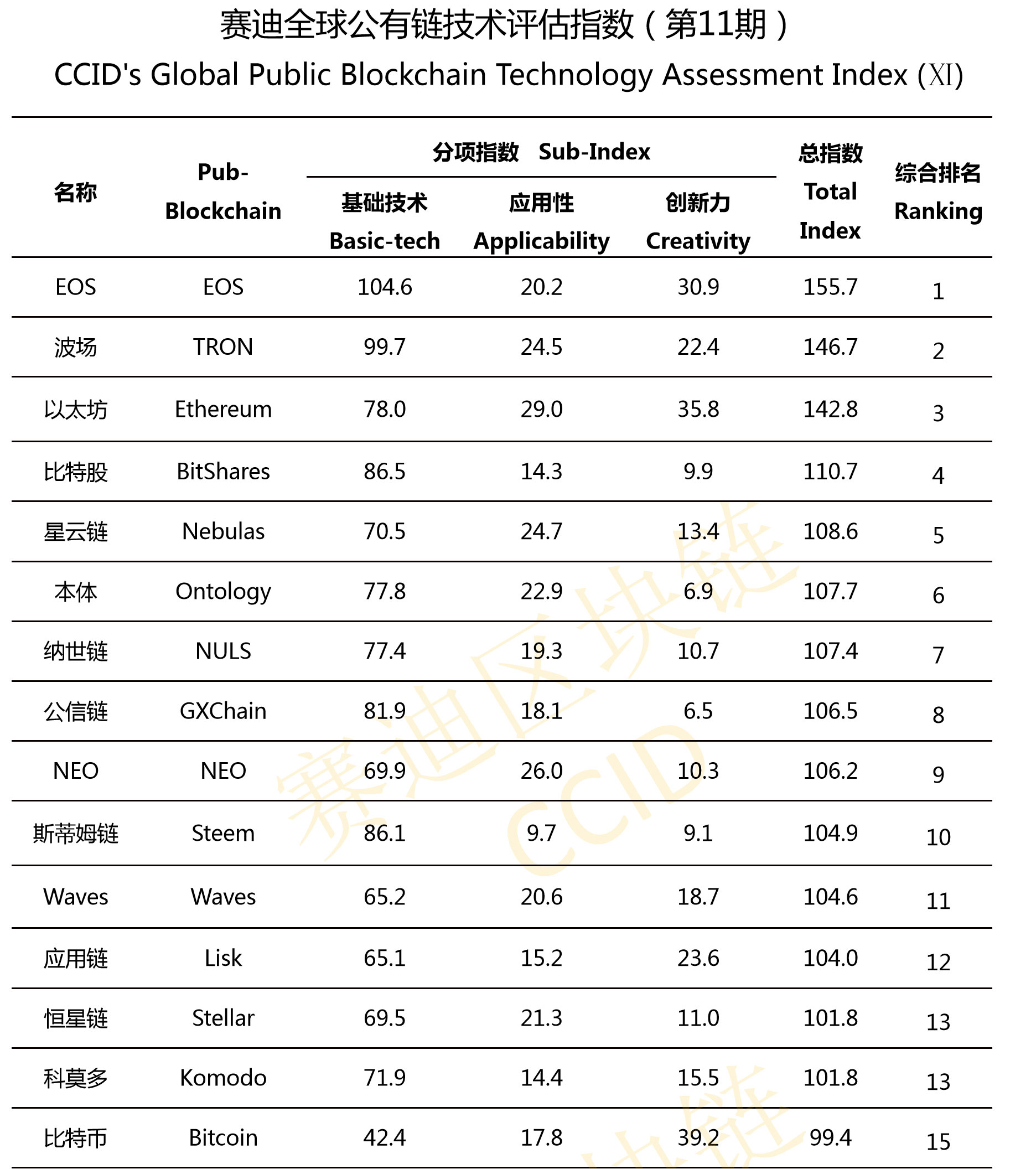
While Bitcoin dropping to 15th out of the 35 crypto assets on CCID’s ranking surprised many investors and analysts, it is important to understand the criteria CCID has been using to find the best blockchain projects from its point of view.
DApp-Focused Approach in Grading Crypto Assets, TRON and EOS Ahead
The top three cryptocurrencies on the CCID ranking are EOS, TRON, and Ethereum, all of which are dApp-focused blockchain networks that enable developers to build decentralized applications using blockchain technology.
The official statement of CCID published on March 22 specifically emphasized that blockchain networks designed to support dApps ranked as the top blockchain networks based on its criteria.
In recent years, many government agencies across the world including China and South Korea have experimented with blockchain technology to potentially run services or applications on a public ledger.
For instance, despite its strict policies on cryptocurrency trading, in September 2018, China’s Ministry of Civil Affairs (MCA) revealed its plans to implement blockchain technology in tracking charity donations for transparency.
The roughly translated document released by MCA read:
“Build a tamper-proof charity organization information query system and enhance the authority, transparency and public trust of information publishing and search services.”
For both government agencies and corporations that require large transaction capacity to process big chunks of data, scalability and flexibility-focused blockchain networks could appeal more than security and payments-focused blockchain networks.
Bitcoin, due to its hashrate or computing power that is supporting the network, is by far the most secure and reliable blockchain network in the market today.

As such, given the track record of Bitcoin and the asset being the first cryptocurrency to guide the blockchain movement, investors may find it difficult to understand Bitcoin being ranked at 15th below cryptocurrencies less than two years old.
More importantly, throughout the past two years, Bitcoin remains as one of the few cryptocurrencies that has seen a consistent increase in its hashrate regardless of the 15-month-long bear market and the Bitcoin Cash versus Bitcoin SV hashrate war that led some of the Bitcoin network’s computing power to drop momentarily.
But, security or historical performance are not a part of CCID’s three major criterions which include basic-tech, applicability, and creativity. The criteria utilized by CCID naturally favors dApp and scalability-focused blockchain networks, hence Bitcoin and other security-focused blockchains ranking below most dApp blockchains.
China’s Shouldn’t Disregard Bitcoin
The ranking of CCID alone does not provide enough context for investors to analyze the performance or the progress of the development of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
It is difficult to create one single criterion for blockchain technology that satisfies all characteristics of a blockchain network, and as such, the CCID crypto ranking should only be taken as a reference, not as a definitive ranking of blockchains.
Based on applicability and creativity which CCID’s criteria features, in the future, it is highly likely that dApps with a higher number of dApps, transaction volume, and capacity will continue to rank higher than others.
But that doesn’t make them right.